1. Campo di applicazione del presente documento
Il presente documento permette a un'azienda di raggiungere i propri obiettivi in fatto di sicurezza dei mangimi. Specifica i requisiti di un Feed Safety Management Systems Requirement (Sistema di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi) [FSMS] che consenta all'azienda di fornire prodotti e servizi sicuri relativamente ai mangimi.
Tutti i requisiti di questo standard sono generici e sono destinati ad essere applicabili a tutte le aziende che operano nella catena mangimistica, indipendentemente dalle loro dimensioni e dalla loro complessità. Queste possono essere aziende che producono additivi per mangimi, materie prime per mangimi, premiscele, mangimi composti o mangimi per animali domestici, ma anche le aziende coinvolte nel commercio, nello stoccaggio, nel trasbordo, e nel trasporto su strada o rotaia di questi prodotti.
Nel creare questo documento è stata utilizzata la norma ISO 22000:2018 Sistemi di gestione per la sicurezza alimentare - Requisiti per qualsiasi organizzazione nella filiera alimentare, che stabilisce i requisiti e le condizioni per un sistema di gestione per la sicurezza alimentare. In una certa misura, gli stessi requisiti e le stesse condizioni si applicano anche a un sistema di gestione che le aziende produttrici di mangimi possono attuare per garantire la sicurezza dei mangimi. La struttura stessa della ISO 22000 spiega a che cosa serva, mentre un certo numero di requisiti e di condizioni sono indicati nella sua stessa dicitura e formulazione. In questo modo, è relativamente facile abbinare queste due norme. È possibile consultare il testo completo della norma all'interno della NEN-EN-ISO 22000, che può essere acquistata dal NEN - www.nen.nl (https://www.nen.nl/en/nen-en-iso-22000-2018-en-248130).
Il presente documento consente a qualsiasi azienda, anche di piccole dimensioni, di impostare un Sistema di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi solido e affidabile. Inoltre, per soddisfare i requisiti di questo standard, è possibile utilizzare risorse interne e/o esterne.
Il presente documento (insieme alle Specifiche tecniche) fa parte del modulo FSA GMP+. Se un'azienda dimostra di essere conforme ai requisiti di questo standard, l'ente certificatore può emettere una certificazione FSA GMP+.
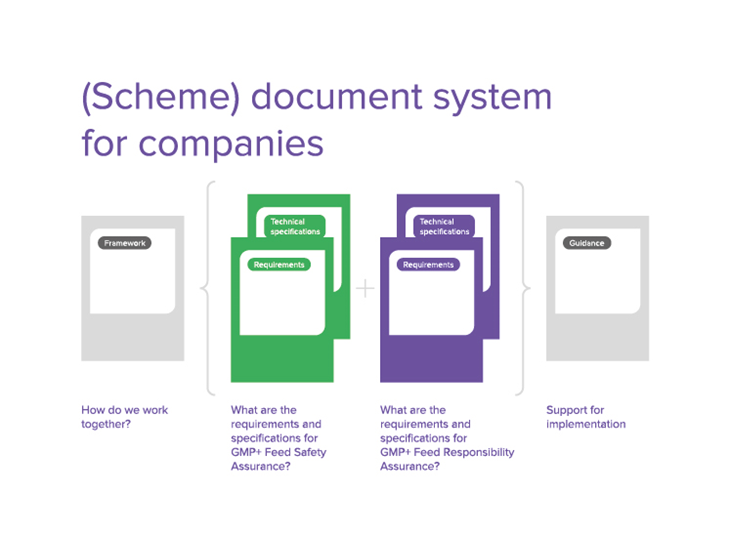
2. Riferimenti normativi
Alcuni requisiti contenuti nel presente documento (i Requisiti dei sistemi di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi) fanno riferimento alle Specifiche tecniche (TS) GMP+. Queste Specifiche tecniche spiegano in maniera più dettagliata uno specifico elemento dei Requisiti dei sistemi di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi e devono essere considerate una parte normativa del modulo FSA GMP+.
Inoltre, alcune Specifiche tecniche si vanno ad aggiungere al presente documento (i Requisiti dei sistemi di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi). Queste Specifiche tecniche devono essere inoltre considerate una parte normativa del modulo FSA GMP+.
3. Termini e definizioni
Vedere F0.2 Elenco definizioni.
4. Il contesto dell’azienda certificata GMP+
Ogni azienda certificata GMP+ fa parte della catena globale mangimistica e di produzione alimentare. L'azienda certificata deve pertanto essere pienamente cosciente di questa posizione. Inoltre, questo è relativo non solo alle sedi in cui si svolgono le attività correlate ai mangimi, ma anche a quelle in cui vengono commercializzati i prodotti dell'azienda garantiti dall’FSA GMP+.
4.1. Conformità con la legislazione sui mangimi e il presente standard
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve rispettare le leggi vigenti in materia di mangimi. Questo è relativo alla legislazione in materia di mangimi:
- nel Paese in cui ha sede l'azienda certificata;
- nel Paese dove il mangime viene commercializzato.
- l'azienda certificata GMP+ deve inoltre attenersi alle sezioni pertinenti dello standard.
Se lo standard non descrive misure di controllo per una situazione specifica, è responsabilità dell'azienda certificata GMP+ stabilire e implementare misure di controllo aggiuntivo sulla base di uno studio HACCP, come descritto nel Capitolo 8.
In tutti i casi di cui sopra, si tratta del requisito più rigoroso applicabile per le aziende certificate GMP+.
4.2. Comprendere le necessità e le aspettative delle parti interessate
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve garantire che i prodotti ei servizi forniti siano conformi ai requisiti applicabili dello GMP+ FC scheme e alle esigenze delle parti interessate pertinenti.
Nuttige tip
Esiste una vasta gamma di parti interessate, le cui necessità devono essere prese in considerazione relativamente al Sistema di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi GMP+. Può essere utile elencarle con attenzione. Queste parti interessate vanno dai fornitori ai clienti, dai trasportatori incaricati ai fornitori di servizi come la disinfestazione, la pulizia dei silos e la pulizia dei serbatoi, dalle imprese portuali agli schemi di certificazione, fino alle autorità portuali.
4.3. Stabilire l’ambito del Sistema di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve stabilire l’ambito del sistema FSMS specificando:
- tutte le attività, i processi, i prodotti o i servizi relativi al mangime di cui è responsabile. Questi includono le attività, i processi, i prodotti e i servizi svolti da/per terzi;
- tutte le sedi, siano esse di proprietà dell'azienda o meno, incluse le sedi amministrative pertinenti;
- quali attività, processi, prodotti o servizi presso tali sedi sono soggetti a certificazione GMP+;
È possibile escludere attività, processi, prodotti o servizi correlati alla produzione, al commercio, allo stoccaggio e al trasporto di mangimi dall’ambito della certificazione GMP+.
- altre attività, processi, prodotti o servizi (relativi o meno ai mangimi), come definiti al paragrafo c) che possono avere un impatto sula sicurezza dei mangimi. L'azienda certificata deve assicurarsi che tali attività, processi, prodotti o servizi non abbiano un impatto negativo sulla sicurezza dei mangimi. Per maggiori dettagli, vedere il Capitolo 1.10 Separazione di TS1.10 Attività operative;
- nello stabilire l’ambito, l'azienda certificata GMP+ deve sempre tenere in considerazione i requisiti menzionati ai paragrafi 4.1 e 4.2.
Tutte le attività che potrebbero influenzare la sicurezza dei mangimi devono essere disponibili per verifiche ispettive. Il campo di applicazione deve essere documentato e aggiornato.
Nuttige tip
Si tratta di una questione complessa. Un ottimo punto di partenza per informarsi sull’ambito delle attività relative alla certificazione GMP+ sono il documenti: F0.3 Campi di applicazione per la certificazione e S9.3 Explanation of GMP+ feed chain (version inglese).
Sopra abbiamo parlato di “attività e/o prodotti che non sono correlati ai mangimi”. In questo caso si può pensare, ad esempio, allo stoccaggio di carburanti, macchine agricole, legna. Si tratta di attività non direttamente legate al processo dei mangimi, ma che potrebbero avere un impatto negativo sulla sicurezza dei mangimi.
4.4. Feed Safety Management System
(Sistema di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi)
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve stabilire, implementare, mantenere, aggiornare e migliorare continuamente un Sistema di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi, in conformità con i requisiti degli standard GMP+. Occorre presentare attenzione all’interazione tra i singoli processi. Il tuo Sistema di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi deve controllare i tuoi processi, inclusa l’interazione tra tali processi.
Quando si utilizzano elementi sviluppati esternamente per creare il tuo Sistema di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi, è necessario assicurarsi, sulla base di una valutazione, che tali elementi siano (resi) idonei per lo specifico Sistema di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi.
Nuttige tip
Gli elementi sviluppati esternamente possono essere (parte di) un manuale di qualità sviluppato da un consulente o da uno studio HACCP o da un Codice deontologico realizzati da un'associazione, ad esempio. Inoltre, pensa alle valutazioni di rischio generico fornite da GMP+ International in Prodotti di supporto sui mangimi.
5. Leadership
5.1. Impegno dell’Alta Dirigenza
L’Alta Dirigenza di un’azienda certificata GMP+ deve garantire:
- l’avvenuta registrazione della politica di sicurezza dei mangimi e degli obiettivi del sistema FSMS;
- l’integrazione dei requisiti del sistema FSMS all’interno dei processi aziendali;
- la disponibilità delle risorse necessarie per rispettare il sistema FSMS e per garantirne il miglioramento continuo;
- la valutazione, il mantenimento e la comunicazione della conformità con il sistema FSMS e con i requisiti dei clienti;
- l’addestramento e il sostegno alle persone affinché possano assumere le responsabilità necessarie per garantire l’efficacia del sistema FSMS.
5.2. Politica sulla sicurezza dei mangimi
5.2.1. Contenuti della politica sulla sicurezza dei mangimi
La politica sulla sicurezza dei mangimi messa in atto e mantenuta dall’Alta Dirigenza deve:
- garantire la conformità con i documenti GMP+ pertinenti, con le leggi applicabili (in materia di mangimi) e con i requisiti dei clienti;
- adattarsi al contesto e agli obiettivi dell’organizzazione;
- comprendere una struttura atta a definire e valutare gli obiettivi del sistema FSMS, secondo quanto descritto nel Capitolo 6;
- comprendere le comunicazioni interne ed esterne applicabili al sistema FSMS;
- comprendere l’impegno al miglioramento continuo del sistema FSMS e la necessaria conoscenza in materia di sicurezza dei mangimi;
5.2.2. Comunicazioni sulla politica di sicurezza dei mangimi
La politica sulla sicurezza dei mangimi deve:
- essere conservata tra le informazioni documentate;
- essere comunicata e applicata all’interno dell’azienda certificata GMP+;
- essere messa a disposizione delle parti interessate.
5.3. Responsabilità
5.3.1. Responsabilità dell’Alta Dirigenza
L’Alta Dirigenza deve fare in modo che le responsabilità e le autorità legate ai ruoli rilevanti siano assegnate, comunicate e comprese all’interno dell’azienda. L’Alta Dirigenza è responsabile in ultima sede del Sistema di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi L’Alta Dirigenza deve stabilire responsabilità e autorità per:
- assicurare che il sistema FSMS sia conforme ai requisiti GMP+;
- creare il/i Feed Safety Team (team di sicurezza dei mangimi) e il/i rispettivo/i leader. In presenza di più di un Feed Safety Team, occorre assegnare un coordinatore;
- creare il/i Team di Convalida e il/i rispettivo/i leader. Nonostante i membri del Feed Safety Team possano anche essere membri del Team di Convalida, quest’ultimo deve essere composto almeno da un membro indipendente per scongiurare indebite ingerenze. Qualora ciò non sia possibile, l’Alta Dirigenza può deviare da questa norma a condizione che vengano fornite giustificazioni valide. In presenza di più di un team di convalida, occorre assegnare un coordinatore;
- nominare soggetti in grado di avviare e documentare eventuali azioni.
5.3.2. Responsabilità del leader del Feed Safety Team
Il leader del Feed Safety Team ha la responsabilità di:
- il sistema FSMS (incluso il piano di controllo dei pericoli descritto nel par. 8.5) venga messo in pratica e aggiornato;
- le attività del Food Safety Team siano coordinate;
- al Feed Safety Team siano garantite la formazione e le competenze necessarie (par. 7.2);
- l’Alta Dirigenza sia informata in merito alle prestazioni del sistema FSMS e dell’eventuale necessità di miglioramento;
- il sistema FSMS possa contare su coordinamento, progresso, impostazione e mantenimento in caso di presenza di più di un Feed Safety Team.
Nuttige tip
Alcuni membri del personale possono ricoprire svariati ruoli all’interno di un team di sicurezza dei mangimi. Inoltre, è possibile ricorrere anche a risorse esterne all'azienda. Tuttavia, l’Alta Dirigenza rimane responsabile del sistema FSMS.
5.3.3. Responsabilità del Team di Convalida
Il Team di Convalida è tenuto a documentare in modo inequivocabile i membri del team e le rispettive attività.
5.3.4. Responsabilità di tutte le persone coinvolte
Chiunque all’interno dell’azienda certificata GMP+ è tenuto a comunicare alla dirigenza eventuali problematiche, potenziali e reali, relative al sistema FSMS.
6. Pianificazione
6.1. Obiettivi del sistema FSMS
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve fissare gli obiettivi per il sistema FSMS ai rispettivi livelli e ruoli.
Gli obiettivi del sistema FSMS devono:
- essere coerenti con la politica sulla sicurezza dei mangimi e con i requisiti giuridici applicabili, secondo quanto indicato nel Capitolo 4;
- essere quantificabili;
- essere monitorati e verificati;
- essere comunicati;
- essere adeguatamente mantenuti e sottoposti a revisione;
- essere conservati tra le informazioni documentate.
Nuttige tip
Quando inizialmente si pianifica come raggiungere gli obiettivi del sistema FSMS, è una buona idea impostare quanto segue nell’ambito del piano di progetto:
- le attività da svolgere;
- le risorse necessarie;
- i responsabili;
- le tempistiche di realizzazione;
- la valutazione dei risultati.
6.2. Modifiche al sistema FSMS
Qualora si rendessero necessarie modifiche al sistema FSMS, l’azienda certificata GMP+ deve tener conto di quanto segue:
- l’obiettivo delle modifiche e le rispettive potenziali ripercussioni sulla sicurezza dei mangimi;
- L’invariata integrità del sistema FSMS;
- le risorse necessarie;
- i ruoli e le responsabilità assegnate.
7. Assistenza
7.1. Risorse
7.1.1. Generalità
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve stabilire e fornire le risorse necessarie per impostare, implementare, mantenere, aggiornare e migliorare continuamente il sistema FSMS. L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve tener conto di quanto segue:
- la capacità e i limiti delle risorse interne;
- l’eventuale necessità di risorse esterne.
Nuttige tip
Nel presente documento con il termine “risorse” si intendono le persone, l’infrastruttura, l’ambiente di lavoro e altri elementi necessari al fine di creare un Sistema di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi con cui lavorare.
7.1.2. Personale
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve garantire la competenza del personale cui è assegnata la responsabilità di gestire il sistema FSMS e mantenere il medesimo in efficienza. La suddetta competenza deve essere conservata tra le informazioni documentate.
In caso di impiego di personale esterno per la realizzazione delle attività legate al sistema FSMS, l’azienda certificata GMP+ deve mantenere informazioni documentate relativamente agli accordi o ai contratti in cui sono definite le competenze, le responsabilità e le autorità assegnate al suddetto personale.
7.1.3. Infrastruttura
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve fornire le risorse per determinare e mantenere l’infrastruttura necessaria a garantire il rispetto dei requisiti del sistema FSMS. L’infrastruttura può includere:
- strutture (come aree di produzione e stoccaggio, vani di carico);
- attrezzature (tra cui hardware e software);
- tecnologia informatica e per le comunicazioni.
Nota: per maggiori dettagli, consultare TS1.1 Programma di prerequisiti, Capitolo 1 Infrastruttura.
7.1.4. Ambiente di lavoro
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve fornire le risorse previste per realizzare un ambiente di lavoro in cui sia garantito il rispetto dei requisiti del sistema FSMS.
Nuttige tip
L’adeguatezza dell’ambiente di lavoro dipende da elementi umani e fisici, tra cui, per esempio, igiene, temperatura, umidità, luce naturale, condizioni dell’aria e rumore. L’adeguatezza dell’ambiente di lavoro dipende da elementi umani e fisici, tra cui, per esempio, igiene, temperatura, umidità, luce naturale, condizioni dell’aria e rumore
Nota: per maggiori dettagli, consultare TS1.1 Programma di prerequisiti, Capitolo 2 Manutenzione.
7.1.5. Gestione dei fornitori
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve:
- stabilire e applicare i criteri per valutare, selezionare, monitorare le prestazioni e rivalutare i fornitori esterni di processi, prodotti e/o servizi, che possono avere un impatto sulla sicurezza dei mangimi. Questi criteri devono essere basati sull'analisi dei rischi (vedere Capitolo 8). Occorre soddisfare almeno i seguenti requisiti. L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve acquistare processi, prodotti e/o servizi da fornitori:
- con certificazione FSA GMP+ o
- con certificazione per un altro standard accettato, oppure;
- garantiti da un'azienda certificata GMP+ tramite condizioni gatekeeper. Vedere TS1.2. Acquisto per requisiti specifici.
- garantire una comunicazione adeguata dei requisiti al/i fornitore/i esterno/i;
- garantire che i processi, prodotti o servizi forniti esternamente non influenzino negativamente la capacità GMP+ dell'azienda certificata di soddisfare costantemente i requisiti del sistema FSMS.
Le materie prime per mangimi prodotte o acquistate devono essere incluse in TS1.3 Elenco prodotti. Questo non vale per le materie prime per mangimi che vengono lavorate esclusivamente in mangimi per animali non destinati alla produzione alimentare. I prodotti il cui uso è vietato nei mangimi sono indicati in TS1.4 Prodotti e carburanti vietati.
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve mantenere informazioni documentate relative alla valutazione dei fornitori e delle eventuali azioni necessarie a questo proposito.
Nuttige tip
Quando parliamo di “fornitori esterni” intendiamo tutti i processi, i prodotti e i servizi che l'azienda acquista da fornitori necessari per contribuire alla produzione e/o alla fornitura di mangime garantito GMP+. Questo include anche i fornitori di materie prime, di prodotti medici veterinari, agenti detergenti e servizi esternalizzati come la disinfestazione e la manutenzione.
I documenti di supporto S9.3 Spiegazione della catena mangimistica GMP+ e S9.7 Come svolgere le valutazioni dei fornitori sono molto utili e forniscono maggiori informazioni.
7.2. Competenza
Al fine di garantire la sicurezza dei mangimi e l’efficacia del sistema FSMS, l’azienda certificata GMP+ deve:
- illustrare in modo chiaro le modalità di organizzazione del personale coinvolto;
- individuare le competenze previste per il personale, sia interno che esterno;
- garantire che il personale, nessuno escluso, abbia la competenza prevista in base alla propria istruzione, formazione e/o esperienza;
- garantire che il Feed Safety Team abbia le conoscenze e l’esperienza necessarie per l’implementazione del sistema FSMS. Sono inclusi (ma non solo) i prodotti, i processi, le attrezzature dell’azienda e i pericoli relativi alla sicurezza di mangimi nell’ambito del sistema FSMS;
- ove applicabile, acquisire la competenza necessaria e valutare l’efficacia delle azioni intraprese;
- mantenere prove della competenza tra le informazioni documentate.
Nuttige tip
Quando parliamo di “azioni per acquisire la competenza necessaria”, ci riferiamo al personale che potrebbe aver ricevuto istruzione, formazione e coaching in materia. In assenza di queste conoscenze all’interno dell'azienda, si consiglia di valutare l'assunzione o la consulenza da parte di professionisti competenti.
7.3. Presa di coscienza
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve assicurarsi che il personale, sia interno che esterno, incaricato di occuparsi del sistema FSMS abbia consapevolezza di:
- la politica di sicurezza dei mangimi;
- gli obiettivi del sistema FSMS pertinenti alle proprie attività;
- l’influenza da esse esercitata sull’efficacia del sistema FSMS;
- le ripercussioni dell’eventuale mancato rispetto dei requisiti del sistema FSMS.
7.4. Comunicazione
7.4.1. Generalità
Nel definire le comunicazioni interne ed esterne relative al sistema FSMS, l’azienda certificata GMP+ è tenuta a indicare quali informazioni comunicare, le tempistiche di comunicazione, i responsabili, la metodologia di comunicazione e il/i gruppo/i destinatario/i della comunicazione stessa.
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve assicurarsi che il personale, sia interno che esterno, incaricato di occuparsi del sistema FSMS comprenda la necessità di avere una comunicazione efficace.
7.4.2. Comunicazione esterna
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve mantenere comunicazioni efficaci in merito alla sicurezza dei mangimi con i seguenti soggetti:
- i fornitori di prodotti e servizi nonché i clienti in merito a:
- informazioni sui prodotti per garantire adeguate procedure di manipolazione, stoccaggio, distribuzione e utilizzo del prodotto all’interno della catena mangimistica;
- lo status dei mangimi e servizi FSA GMP+ (Vedere TS1.8 Etichettatura per requisiti specifici);
- pericoli riscontrati per la sicurezza dei mangimi su prodotti/servizi che devono essere controllati da altre aziende all’interno della catena mangimistica;
- disposizioni contrattuali, richieste e ordini, incluse le relative modifiche;
- riscontri, inclusi i reclami;
- mancato rispetto/superamento degli standard o altre irregolarità/non conformità (vedere par. 8.7.2. Gestione dei prodotti potenzialmente pericolosi).
- autorità competenti coinvolte;
- altre organizzazioni pertinenti per il sistema FSMS.
L’azienda certificata GMP+ è tenuta a conservare qualsiasi comunicazione con l’esterno relativa al sistema FSMS tra le informazioni documentate.
Nuttige tip
Forse può essere utile ricordare che l’Ente certificatore dell'azienda certificata GMP+ viene considerato come appaltatore.
7.4.3. Comunicazione interna
L’azienda certificata GMP+ è tenuta a realizzare un sistema di comunicazioni efficace al fine di fornire informazioni puntuali sulle questioni relative alla sicurezza dei mangimi alle funzioni interne dell’organizzazione, in particolare al Feed Safety Team.
Il Feed Safety Team deve inserire le informazioni pertinenti all’atto dell’aggiornamento del sistema FSMS (par. 4.4 e 10.3).
L’Alta Dirigenza deve inserire le informazioni pertinenti come dati di ingresso per il Riesame della Direzione (par. 9.3).
7.5. Informazioni documentate
7.5.1. Generalità
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve inserire nel sistema FSMS le informazioni documentate relative a:
- la politica sulla sicurezza dei mangimi e gli obiettivi in materia di sicurezza dei mangimi;
- i requisiti dello schema GMP+;
- la rilevazione effettuata per valutare l’efficacia del sistema FSMS;
- le informazioni previste dalla legislazione nazionale e internazionale e dai clienti;
- l’ambito di applicazione del sistema FSMS (Capitolo 4).
Nuttige tip
Sono diversi i fattori in grado di influenzare la quantità di informazioni documentate nel sistema FSMS mantenuto dalle aziende certificate GMP+, tra cui:
- le dimensioni dell’azienda;
- la tipologia di attività, processi, prodotti e servizi e la rispettiva complessità;
- la competenza del personale.
7.5.2. Creazione e aggiornamento
Le informazioni documentate dell’azienda certificata GMP+ devono:
- essere identificate (per es. titolo, data, autore o numero di riferimento);
- essere redatte in formato adeguato (per es. lingua, versione software, grafica) e su supporto idoneo (per es. cartaceo, elettronico);
- contenere informazioni adeguate e idonee.
7.5.3. Controllo di informazioni documentate
Le informazioni documentate previste dal sistema FSMS che l’azienda certificata GMP+ è tenuta a mantenere devono essere disponibili, idonee all’uso e protette (per es. dall’eventuale perdita di riservatezza, dall’uso improprio o dalla perdita d’integrità).
Per il controllo delle informazioni documentate, l'azienda certificata GMP+ deve occuparsi di quanto segue, secondo i casi:
- distribuzione, accesso, recupero e utilizzo;
- archiviazione e conservazione, inclusa la conservazione della leggibilità;
- controllo delle modifiche (ad es. controllo della versione);
- conservazione ed eliminazione. Le informazioni documentate devono essere conservate per almeno tre anni, a meno che non sia richiesto un periodo di conservazione più lungo in base alla legislazione vigente in materia di mangimi o altre normative.
È necessario individuare e controllare le informazioni documentate di origine esterna che l’azienda certificata GMP+ riconosca come necessarie per la pianificazione e la gestione del sistema FSMS. Le informazioni documentate conservate come prove di conformità devono essere protette da alterazioni involontarie.
8. Operazioni
8.1. Pianificazione e controllo delle operazioni
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve pianificare, implementare, controllare, mantenere e aggiornare i processi necessari per rispettare i requisiti per la realizzazione di prodotti per mangimi sicuri come segue:
- aggiornando i criteri per i processi;
- implementando il controllo dei processi secondo i criteri;
- mantenendo informazioni documentate al fine di dimostrare che i processi sono stati svolti secondo pianificazione.
L’azienda certificata GMP+ è tenuta a controllare le modifiche pianificate e a riesaminare le conseguenze di modifiche involontarie, provvedendo ad attenuare gli eventuali effetti negativi.
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve garantire che i processi esternalizzati siano controllati (vedere par. 4.3).
8.2. Programma di prerequisiti (PRP)
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve stabilire Programmi di prerequisiti (PRP) che siano:
- idonei all’organizzazione e al suo contesto per quanto concerne la sicurezza dei mangimi;
- idonei alle dimensioni e alla tipologia di operazioni e alla natura dei prodotti realizzati, stoccati e/o trasportati;
- realizzati all’interno dell’organizzazione sulla base del campo di applicazione del sistema FSMS;
- approvati dal team di sicurezza dei mangimi;
- conformi alle normative applicabili in materia di sicurezza dei mangimi e alle esigenze dei clienti (vedere il Capitolo 4).
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve tener conto degli elementi di seguito nel definire i Programmi di prerequisiti (PRP):
- la struttura, la disposizione degli edifici, ivi compresi i locali per i dipendenti;
- le forniture di aria, acqua, energia e altre utenze;
- la disinfestazione, lo smaltimento di rifiuti e acque reflue e i servizi di supporto;
- l’idoneità delle attrezzature così come la rispettiva pulizia e manutenzione;
- la prevenzione della contaminazione crociata;
- la pulizia e la disinfestazione;
- l’igiene personale;
- informazioni sui prodotti/consapevolezza dei consumatori;
- altri fattori, secondo i casi.
I Programmi di prerequisiti (PRP) devono almeno essere conformi a TS1.1 Programma di prerequisiti. L’azienda certificata GMP+ è responsabile della selezione dei requisiti applicabili.
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve tenere informazioni documentate sulla messa in atto, il monitoraggio e la verifica dei programmi di prerequisiti (PRP).
8.3. Sistema di tracciabilità
Tutti i prodotti che possono avere un impatto sulla sicurezza dei mangimi (mangimi garantiti FSA GMP+ o non garantiti FSA GMP+) devono essere tracciabili in tutte le fasi della produzione. Il sistema di tracciabilità deve essere in grado di individuare le fasi che vanno dall’ingresso del materiale in arrivo dai fornitori alla consegna del prodotto finito.
Per maggiori dettagli, consultare TS1.1 Programma di prerequisiti, Capitolo 10 Sistema di tracciabilità.
Le informazioni richieste devono essere a disposizione di GMP+ International e delle autorità competenti entro 4 ore, a meno che le autorità non fissino tempi più brevi.
Le informazioni documentate come prova del sistema di tracciabilità devono essere conservate per un periodo di tempo specificato al par. 7.5. L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve verificare l'efficacia del sistema di tracciabilità.
Se l'azienda certificata GMP+ è titolare della merce, devono essere prelevati campioni dal mangime in entrata e/o in uscita secondo il TS1.6 Campionatura. Occorre prelevare un campione dal mangime in entrata e in uscita, se questo viene rinviato in un formato diverso da quello in cui è stato ricevuto. I campioni devono essere tenuti a disposizione per l'autorità competente. L'azienda certificata può stipulare contratti scritti con soggetti terzi per il prelievo e la conservazione di campioni.
Nuttige tip
Il documento di supporto S9.8 Come sviluppare sistemi di tracciabilità è molto utile e fornisce maggiori informazioni su come impostare una procedura di tracciabilità interna.
Nuttige tip
Il periodo di 4 ore di cui sopra significa che non appena l'azienda certificata riceve la richiesta di fornire le informazioni necessarie, questa avrà un massimo di 4 ore (consecutive) per fornirle.
8.4. Gestione degli incidenti
8.4.1. Generalità
L’Alta Dirigenza deve predisporre delle procedure al fine di rispondere a potenziali incidenti che possono avere un impatto sulla sicurezza dei mangimi o sul ruolo dell’azienda certificata GMP+ all’interno della catena mangimistica.
L’azienda certificata GMP+ è tenuta a conservare informazioni documentate per la gestione di questi incidenti.
8.4.2. Interventi in caso di incidenti
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve:
- rispondere in caso di incidente mediante:
- individuazione dei requisiti giuridici applicabili;
- comunicazione all’interno dell’azienda;
- comunicazione alle parti interessate (per es. fornitori, clienti, autorità competenti, media).
- ridurre le conseguenze dell’incidente (vedere par.8.7.2)
- riesaminare e, ove necessario, aggiornare le informazioni documentate dopo un incidente o un collaudo.
Nota: gli incidenti legati alla sicurezza dei mangimi comprendono: catastrofi naturali, infortuni sul posto di lavoro, emergenze legate alla sanità pubblica e interruzione di forniture essenziali quali acqua, elettricità o condizionamento.
8.5. Controllo dei pericoli
8.5.1. Attività propedeutiche all’analisi dei pericoli
8.5.1.1. Descrizione degli ingredienti
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve mantener aggiornate le informazioni documentate relative a tutte le materie prime per mangimi, a tutti gli additivi per mangimi e ai coadiuvanti tecnologici nella misura necessaria per individuare i pericoli e svolgere una valutazione del rischio (vedere par. 8.5.2.2). Occorre documentare le seguenti informazioni:
- caratteristiche microbiologiche, chimiche e fisiche;
- composizione degli ingredienti per mangimi, inclusi additivi e coadiuvanti tecnologici;
- origine (ad es. animale, minerale, vegetale, fermentazione, ecc.);
- luogo di origine (provenienza);
- metodo di produzione.;
- confezionamento;
- metodo di consegna;
- condizioni di stoccaggio e durata a magazzino;
- preparazione e/o manipolazione prima dell’uso o della lavorazione;
- limiti di sicurezza specifici per gli ingredienti dei mangimi, additivi per mangimi e coadiuvanti tecnologici (TS1.5 Limiti di sicurezza specifici dei mangimi);
- requisiti legali (vedere par. 4.1);
- nome del prodotto o simile identificativo.
8.5.1.2. Descrizione dei prodotti finali
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve mantenere aggiornate le informazioni documentate relative ai prodotti finali nella misura necessaria per condurre una valutazione del rischio (vedere par. 8.5.2.2). Occorre documentare le seguenti informazioni:
- nome del prodotto o simile identificativo;
- composizione del mangime: ingredienti e sostanze ausiliarie utilizzati (inclusi additivi per mangimi e coadiuvanti tecnologici);
- caratteristiche biologiche, chimiche e fisiche;
- condizioni di stoccaggio e durata a magazzino;
- imballaggio;
- etichettatura relativa alla sicurezza dei mangimi e/o istruzioni per la manipolazione, la preparazione e l’uso previsto;
- metodo di distribuzione e fornitura;
- requisiti legali (vedere par. 4.1);
- limiti di sicurezza per i mangimi (TS1.5 Limiti di sicurezza specifici dei mangimi).
8.5.1.3. Uso previsto
L’uso previsto deve essere considerato e conservato come informazione documentata nella misura necessaria per condurre una valutazione del rischio (vedere par. 8.5.2.2). Occorre documentare le seguenti informazioni:
- uso previsto;
- istruzioni di preparazione;
- istruzioni per la somministrazione (se del caso: inclusi i periodi di sospensione);
- condizioni di stoccaggio;
- condizioni relative al trasporto e al luogo di consegna;
- durata a magazzino;
- informazioni richieste per legge sulla confezione e/o sui documenti di accompagnamento;
- manipolazione errata o utilizzo scorretto del prodotto ragionevolmente prevedibili.
Nuttige tip
Un esempio di utilizzo scorretto del prodotto è somministrare alle pecore con elevato contenuto di rame per capre e altro bestiame. Le pecore rischiano l'avvelenamento a causa del consumo di mangime con elevato contenuto di rame. Questa è una delle più comuni cause di avvelenamento nelle pecore.
8.5.1.4. Diagrammi di flusso e descrizione dei processi
Il Feed Safety Team deve creare, mantenere e aggiornare diagrammi di flusso e una planimetria come informazioni documentate per ciascun mangime (gruppo) e ingrediente per mangimi (gruppo).
Per l'analisi dei pericoli, occorre utilizzare diagrammi di flusso come strumento di identificazione e valutazione dei pericoli per la sicurezza dei mangimi.
Nuttige tip
É possibile creare gruppi di prodotti. Quando si creano gruppi di prodotti, occorre combinare prodotti con le stesse caratteristiche, realizzati con processi simili. Nella creazione dei gruppi, occorre accertarsi di non trascurare i rischi specifici dei singoli prodotti.
8.5.1.4.1. Preparazione dei diagrammi di flusso
I diagrammi di flusso devono essere sufficientemente dettagliati per consentire un’analisi dei pericoli. I diagrammi di flusso devono comprendere:
- la rappresentazione delle singole fasi presenti nella sequenza di processo (dall'acquisto alla consegna), i resi del cliente, le rilavorazioni, il riciclaggio e i rifiuti eventualmente prodotti durante il processo;
- eventuali processi esternalizzati;
- dove le materie prime, gli ingredienti, i coadiuvanti tecnologici, i materiali, le utenze e i prodotti intermedi entrano a far parte del flusso;
- il luogo in cui vengono realizzati i prodotti finali, i prodotti intermedi e i sottoprodotti.
8.5.1.4.2. Preparazione di una planimetria
Se del caso, occorre indicare in una planimetria l’intera infrastruttura della sede aziendale, inclusi:
- unità di produzione, aree di stoccaggio e strutture per il personale;
- macchinari e attrezzature;
- percorsi di mangime e materie prime all’interno dell’azienda per rendere visibili eventuali punti di contaminazione incrociata.
8.5.1.4.3. Validazione dei diagrammi di flusso e della planimetria
Il Feed Safety Team deve convalidare in loco l’accuratezza dei diagrammi di flusso e della planimetria, aggiornandoli se del caso e conservandoli tra le informazioni documentate.
Il Feed Safety Team può delegare tale operazione al Team di Convalida o a un altro rappresentante competente in materia di processo/i e di sistema HACCP.
8.5.2. Analisi dei pericoli
8.5.2.1. Individuazione dei pericoli
Il Feed Safety Team deve individuare e documentare tutti i pericoli per la sicurezza dei mangimi che potrebbero incidere negativamente sulla sicurezza del prodotto, sul tipo di lavorazione e sull’ambiente di lavorazione.
Questa procedura si basa su:
- le informazioni e i dati raccolti durante le precedenti fasi dell’HACCP (par. 8.5.1);
- l’esperienza;
- le informazioni interne ed esterne di pertinenza, ivi compresi i dati epidemiologici, scientifici e altri dati storici;
- le informazioni dalla catena mangimistica sui pericoli per la sicurezza dei mangimi relativi alla sicurezza dei prodotti finali, dei prodotti intermedi e dei mangimi e degli alimenti al momento del consumo;
- i requisiti legali;
- la valutazione generica del rischio da Prodotti di supporto sui mangimi (FSP);
- le schede informative di sostanze e prodotti indesiderabili da Prodotti di supporto sui mangimi (FSP).
I pericoli devono essere analizzati in sufficiente dettaglio da rendere possibile la valutazione del rischio e la selezione di misure di controllo adeguato.
Per ciascuna fase del processo il Feed Safety Team deve individuare il pericolo eventualmente presente, introducibile, aumentabile o rimanente.
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve individuare i pericoli eventualmente presenti:
- nei passaggi precedenti e successivi della catena mangimistica;
- in tutte le fasi previste nel diagramma di flusso;
- nelle attrezzature di processo, nell’infrastruttura, nell’ambiente di lavorazione e per il personale.
Per ciascun pericolo, il Feed Safety Team deve anche stabilire e registrare un limite di sicurezza dei mangimi per cui si assicuri come minimo la conformità ai limiti legali di sicurezza dei mangimi e ai limiti indicati in TS1.5 Limiti di sicurezza specifici dei mangimi.
8.5.2.2. Valutazione del rischio
Il Feed Safety Team è tenuto a condurre una valutazione del rischio per ciascun pericolo riscontrato che abbia un impatto sulla sicurezza dei mangimi oltre a stabilire se la prevenzione o la riduzione del pericolo a un livello accettabile sia un fattore critico per produrre mangimi sicuri.
Per ciascun pericolo per la sicurezza dei mangimi l’azienda certificata GMP+ deve stabilire quanto segue:
- la probabilità che si verifichi nel prodotto finale prima dell’applicazione delle misure di controllo;
- la gravità degli eventuali effetti avversi del pericolo sulla sicurezza dei mangimi.
Occorre descrivere la metodologia utilizzata per la valutazione del rischio e il risultato della stessa deve essere conservato tra le informazioni documentate.
Nuttige tip
Il documento di supporto S9.4 Applicazione della valutazione HACCP costituisce un esempio utile di metodologia per la valutazione del rischio. Le aziende certificate GMP+ possono utilizzare questa o un'altra metodologia per svolgere la valutazione del rischio.
8.5.2.3. Determinazione dei punti di controllo critico (CCP)
Il Feed Safety Team deve inoltre stabilire una o più misure di controllo adeguate al fine di prevenire i pericoli sulla sicurezza dei mangimi o ridurne l’entità entro limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi predefiniti.
Per ciascuna misura di controllo, il Feed Safety T deve stabilire se questa misura di controllo è la misura finale nel processo di controllo di tale pericolo. Se lo è, allora verrà chiamata Punto di controllo critico (CCP). Le motivazioni per la creazione di un Punto di controllo critico (CCP) devono essere documentate.
Il processo decisionale e l’esito della definizione delle misure di controllo devono essere documentati.
Nuttige tip
I punti di controllo critici (CCP) possono essere creati anche con l'aiuto di uno schema decisionale come indicato nel documento S9.4 Applicazione della valutazione HACCP.
8.5.3. Controllo CCP
8.5.3.1. Definizione dei limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi per i CCP
Per stabilire se una misura di controllo funziona correttamente, il Feed Safety T deve stabilire quanto segue per ogni Punto di controllo critico (CCP):
- quali parametri occorre misurare, analizzare od osservare, e
- quali limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi si applicano per tali parametri.
Quando si stabiliscono i limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi, l’azienda certificata GMP+ deve:
- garantire l’individuazione dei requisiti normativi e di legge applicabili;
- garantire che i limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi applicabili vengano individuati secondo quanto previsto nel modulo FSA GMP+ (TS1.5 Limiti di sicurezza specifici dei mangimi);
- considerare l'uso previsto dei prodotti finali;
- considerare qualsiasi altra informazioni pertinente.
La logica alla base della scelta di specifici Limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi da parte dell’azienda certificata GMP+ deve essere conservata come informazione documentata.
Se non vi sono limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi previsti per legge o da GMP+ per un determinato tipo di mangime, le aziende certificate hanno la responsabilità di fissare limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi nel proprio studio HACCP.
La ricerca deve essere fondata su studi basati sulla letteratura, informazioni di settore, ecc.
Se esiste un limite di sicurezza dei mangimi sia dettato dalla legge che da GMP+ per un determinato tipo di mangime, si applica il limite di sicurezza dei mangimi più rigoroso tra i due.
8.5.3.2. Monitoraggio dei CCP
Occorre impostare, per ciascun CCP, un piano di monitoraggio per ogni misura di controllo al fine di rilevare l’eventuale mancata permanenza all’interno dei limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi. Il piano di monitoraggio deve comprendere tutte le analisi relative ai limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi.
Il piano di monitoraggio deve essere composto da informazioni documentate, tra cui:
- analisi od osservazioni che forniscano risultati entro un lasso temporale adeguato;
- i metodi di campionatura;
- la frequenza della campionatura;
- responsabilità e autorità correlate alla campionatura;
- metodi o attrezzature di monitoraggio utilizzati;
- metodi di calibrazione o metodi equivalenti per la verifica di analisi od osservazioni affidabili;
- frequenza di monitoraggio;
- risultati di monitoraggio;
- responsabilità e autorità correlate al monitoraggio;
- responsabilità e autorità correlate alla valutazione dei risultati di monitoraggio.
Il metodo e la frequenza di monitoraggio su ciascun CCP deve essere in grado di rilevare quanto più rapidamente possibile l’eventuale mancato rispetto dei limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi.
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve garantire adeguate procedure di identificazione e stoccaggio dei campioni prelevati per il monitoraggio in un arco di tempo adeguato come indicato in TS1.6 Campionatura. I campioni conservati devono essere tenuti a disposizione per l'autorità competente. L'azienda certificata può stipulare contratti scritti con soggetti terzi per il prelievo e la conservazione di campioni.
Il piano di monitoraggio deve almeno essere conforme a TS1.7 Monitoraggio. L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve giustificare la struttura del piano di monitoraggio.
I metodi di monitoraggio devono essere adeguati al conseguimento dei risultati programmati. Se la misurazione e il monitoraggio si svolgono tramite analisi, questa deve essere svolta da un laboratorio approvato (vedere TS1.2 Acquisto).
8.6. Convalida e verifica
8.6.1. Convalida
Il Team di Convalida (vedere par. 5.3.3) deve convalidare il piano HACCP prima della sua implementazione e dopo qualsiasi modifica vi venga apportata. Lo scopo della convalida è quello di garantire che i pericoli determinati dal team di sicurezza dei mangimi siano completi e corretti e che siano efficacemente controllati con le misure di controllo proposte, il piano di monitoraggio e le azioni correttive.
Il Feed Safety Team è tenuto a modificare la/e misura/e di controllo e/o una o più combinazioni delle medesime, procedendo a un’ulteriore valutazione nel caso in cui non siano in grado di prevenire o attenuare il rischio per la sicurezza dei mangimi.
Il Team di Convalida è tenuto, invece, a mantenere tra le informazioni documentate la metodologia di convalida e le prove attestanti l’efficacia della/e misura/e di controllo ai fini della prevenzione o dell’attenuazione del/i rischio/i sulla sicurezza dei mangimi.
Nuttige tip
É utile ricordare che “modificare” può anche significare cambiamenti nelle misure di controllo e/o nelle tecnologie di produzione per le materie prime, nelle descrizioni dei prodotti finali, nei metodi di distribuzione e nell’uso previsto dei prodotti finali.
8.6.2. Verifica
8.6.2.1. Verifica del piano HACCP
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve mettere in atto e mantenere le attività di verifica. Le fasi di preparazione della verifica devono definire gli obiettivi, i metodi, le frequenze e le responsabilità.
La verifica deve essere svolta dal Feed Safety Team e deve dimostrare quanto segue:
- l’efficacia e l’attualità del piano HACCP;
- i livelli di pericolo rientrino nei limiti accettabili identificati;
- la messa in atto e l’efficacia di altre azioni relative al piano HACCP.
8.6.2.2. Analizzare i risultati delle attività di verifica
Laddove i campioni dei prodotti finiti o i campioni prelevati direttamente dalle lavorazioni non rispettino i limiti definiti per la sicurezza dei mangimi (vedere TS1.5 Limiti specifici per la sicurezza dei mangimi), l’azienda certificata GMP+ deve porre in atto le azioni correttive secondo quanto stabilito nel par. 8.7.1.
Il Feed Safety Team deve esaminare i risultati della verifica almeno una volta all’anno, utilizzando gli stessi quali dati in ingresso per il Riesame della Direzione (vedere par. 9.3).
8.7. Controllo dei prodotti e dei processi non conformi
8.7.1. Rettifiche e azioni correttive
Se i limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi non vengono rispettati (cioè in presenza di non conformità), il Feed Safety Team deve specificare correzioni e azioni correttive da adottare e deve garantire che vengano intraprese iniziative per l’eliminazione della non conformità osservata, garantendo che:
- i prodotti potenzialmente pericolosi non vengano commercializzati;
- la causa della non conformità venga individuata;
- il/i parametro/i controllato/i al CCP ritorni/no entro i limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi;
- venga evitata la ricorrenza del problema (verifica dell’azione correttiva).
Il Feed Safety Team deve introdurre correzioni secondo il par. 10.1. Vedere anche il par. 8.7.2. relativamente ai prodotti (potenzialmente) pericolosi.
8.7.2. Gestione dei prodotti potenzialmente pericolosi
8.7.2.1. Generalità
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve intervenire per impedire che prodotti potenzialmente pericolosi entrino nella catena mangimistica e/o di produzione alimentare, a meno che l'azienda certificata GMP+ possa dimostrare che lo/gli specifico/i pericolo/i per la sicurezza dei mangimi sia/no stato/i ridotto/i entro i limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi definiti, come al par. 8.5.3.1.
8.7.2.2. Valutazione dei prodotti potenzialmente pericolosi
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve valutare ciascun lotto di prodotti non conforme al fine di stabilire se i prodotti siano sicuri o meno. I prodotti non possono essere considerati sicuri se:
- i limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi relativamente alle sostanze indesiderabili vengono superati, come indicato nella legislazione e/o in TS1.5 Limiti di sicurezza specifici dei mangimi;
- l'azienda certificata GMP+ ha stabilito che la non conformità o l’irregolarità relativa ad aspetti di sicurezza dei mangimi sono fuori controllo e possono avere conseguenze per altre aziende, anche se non vi è una legislazione e/o secondo T.S1.5 Limiti di sicurezza specifici dei mangimi.
I prodotti che sono sotto il controllo dell'azienda certificata GMP+ e che sono stati determinati come pericolosi devono essere gestiti in conformità con il par. 8.7.1.
I controlli, la valutazione per la commercializzazione dei prodotti e le risposte relative delle parti interessate competenti, oltre all’autorizzazione a trattare prodotti potenzialmente pericolosi devono essere conservati come informazioni documentate.
Se un prodotto viene ritenuto pericoloso, l'azienda certificata GMP+ deve comunicarlo alle parti interessate coinvolte. Se i prodotti non sono più sotto il controllo dell’azienda certificata GMP+, questa deve anche darne comunicazione ai clienti interessati e avviare una procedura di ritiro/richiamo (vedere par. 8.7.2.4).
Se l'azienda certificata GMP+ è proprietaria della merce, questa deve anche informare GMP+ International e l’ente certificatore entro 12 ore dal momento in cui è stato constatato il fatto o se ne è avuta conferma. GMP+ International deve essere informata tramite il modulo di notifica EWS, disponibile sul sito web di GMP+ International.
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve creare e mantenere informazioni documentate per informare GMP+ International, l’ente certificatore e altre parti interessate coinvolte.
Nota: le parti interessate possono, ad esempio, essere autorità legali e di regolamentazione, clienti e/o fornitori. Se l'azienda certificata GMP+ ritiene che la situazione sia sotto controllo, la scadenza di notifica a 12 ore può essere prolungata.
8.7.2.3. Smaltimento dei prodotti non conformi
L’azienda certificata GMP+ è tenuta a gestire i prodotti non conformi secondo una delle opzioni sotto indicate:
- rilavorazione o ulteriore lavorazione affinché i prodotti rispettino i limiti di sicurezza dei mangimi;
- destinazione a uso diverso da mangime; oppure
- distruzione e/o smaltimento come rifiuti.
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve tenere informazioni documentate sulla distruzione / sullo smaltimento dei prodotti non conformi, ivi compresa l’approvazione del/i soggetto/i preposto/i all’autorizzazione.
8.7.2.4. Ritiro/richiamo
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve tenere una procedura documentata di ritiro/richiamo dei prodotti non sicuri in tempi quanto più rapidi possibili (par. 8.7.2.2).
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve conservare informazioni documentate su:
- la notifica inoltrata alle parti interessate di pertinenza;
- la gestione dei prodotti ritirati/richiamati;
- le azioni intraprese.
I prodotti ritirati/richiamati devono essere assicurati o mantenuti sotto il controllo dell'azienda fino a quando vengono gestiti secondo il par. 8.7.2.3.
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve conservare informazioni documentate sulla causa, l’entità e l’esito di un ritiro/richiamo. Queste informazioni devono essere utilizzate come dati in ingresso per il Riesame della Direzione (vedere par. 9.3).
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve verificare la procedura di ritiro/richiamo con cadenza almeno annuale, conservando informazioni documentate a questo proposito.
Per maggior informazioni, vedere il documento di supporto S9.9 Eseguire correttamente un richiamo.
9. Valutazione delle prestazioni del sistema FSMS
9.1. Monitoraggio, misurazione, analisi e valutazione
9.1.1. Generalità
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve valutare le prestazioni e l'efficacia del Sistema di gestione della sicurezza dei mangimi. Questo richiede inoltre di stabilire:
- ciò che deve essere monitorato e misurato;
- i metodi per monitorare, misurare, analizzare e valutare, secondo i casi, al fine di garantire risultati validi;
- quando occorre monitorare e misurare;
- quando occorre analizzare e valutare i risultati dal monitoraggio e dalla misurazione;
- chi deve analizzare e valutare i risultati di monitoraggio e misurazione.
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve conservare adeguate informazioni documentate come prova dei risultati.
9.1.2. Analisi e valutazione
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve esaminare e valutare i risultati derivanti dal monitoraggio e dalle analisi, ivi compresi, come minimo, i risultati delle attività di verifica relativi ai PRP e al piano di controllo dei pericoli (par. 8.6.2), oltre alle verifiche ispettive interne (par. 9.2) ed esterne.
La valutazione deve:
- dimostrare che le prestazioni del sistema FSMS sono conformi ai requisiti stabiliti dall’azienda certificata GMP+;
- stabilire la necessità di aggiornare o migliorare il sistema FSMS;
- individuare la tendenza alla realizzazione di prodotti potenzialmente non sicuri o al verificarsi di guasti di processo;
- raccogliere informazioni per pianificare il programma delle verifiche ispettive interne;
- dimostrare l’efficacia delle rettifiche e delle azioni correttive.
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve conservare tra le informazioni documentate i risultati delle analisi e delle attività intraprese sulla base di queste ultime, e inoltre deve utilizzare tali risultati come dati in ingresso per il Riesame della Direzione (par. 9.3) e per l’aggiornamento del sistema FSMS (par. 10.3).
Nota: per l’analisi dei dati è possibile utilizzare tecniche statistiche.
9.2. Ispettiva interna
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve condurre verifiche ispettive interne a intervalli pianificati per dimostrare che il sistema FSMS:
- è conforme a:
- gli stessi requisiti del sistema FSMS;
- i documenti GMP+;
- sia efficacemente implementato e mantenuto.
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve:
- pianificare, stabilire, porre in atto e mantenere una procedura per le verifiche ispettive interne che comprenda:
- ambito e criteri di verifica;
- una frequenza di verifica pari ad almeno una volta l’anno;
- metodi;
- responsabilità;
- pianificazione di requisiti e reportistica;
- durante lo sviluppo dei programmi di verifica occorre tenere in considerazione:
- l’importanza dei processi previsti;
- le modifiche al sistema FSMS;
- i risultati del monitoraggio e delle precedenti verifiche ispettive;
- la selezione di auditor competenti in grado di garantire l’obiettività e l’imparzialità dell’intero processo di verifica;
- la segnalazione dei risultati delle verifiche ispettive al Feed Safety Team e ai dirigenti competenti;
- la conservazione di informazioni documentate legate al programma di verifiche ispettive e ai risultati delle verifiche;
- la realizzazione delle eventuali rettifiche e azioni correttive entro e non oltre una scadenza prestabilita;
- la corrispondenza del sistema FSMS all’intento della politica di sicurezza dei mangimi (par. 5.2) e agli obiettivi dello stesso FSMS (par. 6.1).
L’azienda certificata GMP+ è tenuta a verificare le azioni intraprese e a segnalare i risultati della verifica.
9.3. Riesame della direzione
9.3.1. Generalità
Il Riesame della Direzione deve essere effettuato dall’Alta Dirigenza sul sistema FSMS con una cadenza pari ad almeno una volta all’anno al fine di garantire l’idoneità, l’adeguatezza e l’efficacia del medesimo FSMS.
9.3.2. Input per il riesame della direzione
Il Riesame della Direzione deve comprendere:
- l’avanzamento delle azioni rispetto ai precedenti riesami della direzione;
- le modifiche all’interno dell'azienda che coinvolgono il sistema FSMS;
- informazioni sulle prestazioni e sull’efficacia del sistema FSMS:
- la conformità a legislazione e normative (par. 4.1);
- gli aggiornamenti del sistema FSMS (par. 4.4. e 10.3);
- i risultati di monitoraggio; e
- i risultati delle attività di verifica relative ai PRP e al Piano HACCP (Capitolo 8);
- la non conformità e azioni correttive;
- i risultati delle verifiche ispettive interne ed esterne;
- le ispezioni (per es. per legge, presso il cliente);
- le prestazioni dei fornitori esterni;
- il raggiungimento degli obiettivi del sistema FSMS;
- l’adeguatezza delle risorse (per es. personale, attrezzature);
- il verificarsi di eventuali allarmi precoci, incidenti (par. 8.4.2) o ritiri/richiami (par. 8.7.2.4);
- informazioni pertinenti relative alla sicurezza dei mangimi, ivi comprese richieste e reclami ricevuti dalle parti interessate (per es. clienti e fornitori) (par. 7.4.2 e par. 7.4.3);
- opportunità di miglioramento continuo.
9.3.3. Esito del riesame della direzione
Gli esiti del Riesame della Direzione devono comprendere:
- decisioni e azioni relative al miglioramento continuo;
- l’eventuale necessità di aggiornamenti e modifiche al sistema FSMS.
L'azienda certificata GMP+ deve conservare adeguate informazioni documentate come prova dei risultati dei riesami della direzione.
10. Miglioramento
10.1. Non conformità e azioni correttive
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve immediatamente:
- reagire alla non conformità e, a seconda dei casi:
- verificare e correggere la stessa;
- gestirne le conseguenze;
- valutare se l’azione/le azioni intrapresa/e per eliminare la/e causa/e della non conformità ne preverranno l’ulteriore insorgenza:
- riesaminando la non conformità;
- definendo la causa scatenante della non conformità;
- determinando se esistono o potrebbero verificarsi simili non conformità;
- implementare eventuali azioni necessarie;
- riesaminare l'efficacia di eventuali azioni correttive adottate;
- aggiornare il sistema FSMS.
Le azioni correttive devono essere tali da risolvere la/e causa/e scatenante/i della non conformità.
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve conservare informazioni documentate in merito a:
- la descrizione della non conformità e delle azioni intraprese;
- i risultati di qualsiasi azione correttiva.
10.2. Miglioramento continuo
L’azienda certificata GMP+ è tenuta al miglioramento continuo del sistema FSMS.
L’Alta Dirigenza è, invece, tenuta a garantire che l’organizzazione migliori il sistema FSMS mediante:
- definizione della politica e degli obiettivi per la sicurezza dei mangimi (Capitolo 4);
- comunicazione (par. 7.4);
- riesami della direzione (par. 9.3);
- risultati delle verifiche ispettive (interne ed esterne) (par. 9.2);
- analisi dei risultati delle attività di verifica (par. 8.6.2);
- convalida della/e misura/e di controllo e della/e combinazione/i di misura/e di controllo (par. 8.6.1.);
- azioni correttive (par. 8.7.1); e
- aggiornamento del sistema FSMS (par. 10.3).
10.3. Aggiornamento dell’FSMS
L’Alta Dirigenza è tenuta a garantire l’aggiornamento continuo del sistema FSMS. Il Feed Safety Team deve valutare il sistema FSMS a intervalli programmati. Il Feed Safety Team deve valutare se sia necessario riesaminare l’analisi dei pericoli (par. 8.5.2), il piano di controllo dei pericoli prestabilito (par. 8.5.3) e i Programmi di prerequisiti (PRP) prestabiliti (par. 8.2). Le attività di aggiornamento devono essere basate su:
- la comunicazione interna ed esterna (par. 7.4);
- altre informazioni relative al sistema FSMS;
- i dati in uscita dalla verifica del sistema FSMS (par. 9.1.2);
- gli esiti del riesame della direzione (par. 9.3).
L’azienda certificata GMP+ deve conservare tra le informazioni documentate le attività di aggiornamento del sistema FSMS, e inoltre deve utilizzare tali informazioni come dati in ingresso per il Riesame della Direzione (par. 9.3).
Risk Management tools
That was a lot of information to digest and one might ask, what is the next step? Luckily we can offer support for the GMP+ Community when doing this. We provide support by means of various tools and guidances but as each company has a shared responsibility to feed safety, and therefor tailor-made solutions cannot be offered. However, we do help by explaining requirements and providing background information about the requirements. □
We have developed various supporting materials for the GMP+ Community. These include various tools, ranging from Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) lists to webinars and events.
Supporting materials related to this document (Guidelines and FAQs)
We have made documents available which give guidance to the GMP+ requirements as laid down in the module GMP+ FSA and GMP+ FRA. These documents give examples, answers to frequently asked questions or background information.
Feed Fraud
Even when all feed safety requirements are applied things can go wrong. Did you even think of the possibility that fraud could have been committed? There is information available that helps you in getting insights on fraud which effects your company, focused on the prevention of feed fraud.
Early Warning System (EWS)
When you detect (possibly) unsafe feed, you have to report this to GMP+ International. Together we can prevent consequential damage to your company and the feed chain (as much as possible). Safe feed is, and remains, a joint responsibility. How this works is explained on our website.
Risk Management tools (RMT)
Risk Management Tools (RMT) provides valuable and up-to-date information about potentially high-risk feed. The products vary from flow charts of production processes including the risks (Risk Assessments) and studies on undesirable substances (fact sheets).
Where to find more about the Risk Management tools? Fact sheets More information: GMP+ Platform Product list More information: Product List Risk Assessments More information: GMP+ Platform GMP+ Monitoring database More information: GMP+ Monitoring database Support documents More information: Support documents |



